Let's do it together, see the following link:
http://vn247.net/flash/people-love.swf
Industrial and Systems Engineering (ISE) aims at imparting fundamental knowledge to develop the ability to address complex industrial issues, emphasising on how to plan, run, control and optimise production systems. This Weblog wants to share the new and critical information on ISE and also wants to invite the expert persons on ISE for participating in writing of the ISE's Weblog.
Saturday, November 25, 2006
What is Process Capability (Cpk)?
Process capability compares the output of an in-control process to the specification limits by using capability indices. The comparison is made by forming the ratio of the spread between the process specifications (the specification "width") to the spread of the process values, as measured by 6 process standard deviation units (the process "width").
A process capability index uses both the process variability and the process specifications to determine whether the process is "capable" . We are often required to compare the output of a stable process with the process specifications and make a statement about how well the process meets specification. To do this we compare the natural variability of a stable process with the process specification limits.
A capable process is one where almost all the measurements fall inside the specification limits. This can be represented pictorially by the plot below: 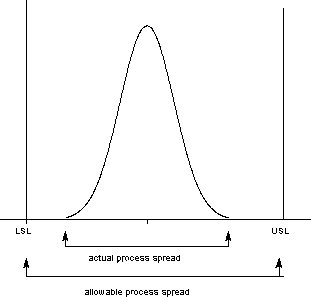
There are several statistics that can be used to measure the capability of a process: Cp, Cpk, Cpm. Most capability indices estimates are valid only if the sample size used is 'large enough'. Large enough is generally thought to be about 50 independent data values.
The Cp, Cpk, and Cpm statistics assume that the population of data values is normally distributed. Assuming a two-sided specification, if and are the mean and standard deviation, respectively, of the normal data and USL, LSL, and T are the upper and lower specification limits and the target value, respectively.
Process Capability Indices
A process capability index uses both the process variability and the process specifications to determine whether the process is "capable" . We are often required to compare the output of a stable process with the process specifications and make a statement about how well the process meets specification. To do this we compare the natural variability of a stable process with the process specification limits.
A capable process is one where almost all the measurements fall inside the specification limits. This can be represented pictorially by the plot below:

There are several statistics that can be used to measure the capability of a process: Cp, Cpk, Cpm. Most capability indices estimates are valid only if the sample size used is 'large enough'. Large enough is generally thought to be about 50 independent data values.
The Cp, Cpk, and Cpm statistics assume that the population of data values is normally distributed. Assuming a two-sided specification, if and are the mean and standard deviation, respectively, of the normal data and USL, LSL, and T are the upper and lower specification limits and the target value, respectively.
Saturday, November 18, 2006
New Technique for Looking at a Decision From All Points of View
Six Thinking Hats
- White Hat: With this thinking hat you focus on the data available. Look at the information you have, and see what you can learn from it. Look for gaps in your knowledge, and either try to fill them or take account of them.This is where you analyze past trends, and try to extrapolate from historical data.
- Red Hat: Wearing' the red hat, you look at problems using intuition, gut reaction, and emotion. Also try to think how other people will react emotionally. Try to understand the responses of people who do not fully know your reasoning.
- Black Hat: Using black hat thinking, look at all the bad points of the decision. Look at it cautiously and defensively. Try to see why it might not work. This is important because it highlights the weak points in a plan. It allows you to eliminate them, alter them, or prepare contingency plans to counter them.
Black Hat thinking helps to make your plans 'tougher' and more resilient. It can also help you to spot fatal flaws and risks before you embark on a course of action. Black Hat thinking is one of the real benefits of this technique, as many successful people get so used to thinking positively that often they cannot see problems in advance. This leaves them under-prepared for difficulties. - Yellow Hat: The yellow hat helps you to think positively. It is the optimistic viewpoint that helps you to see all the benefits of the decision and the value in it. Yellow Hat thinking helps you to keep going when everything looks gloomy and difficult.
- Green Hat: The Green Hat stands for creativity. This is where you can develop creative solutions to a problem. It is a freewheeling way of thinking, in which there is little criticism of ideas.
- Blue Hat:The Blue Hat stands for process control. This is the hat worn by people chairing meetings. When running into difficulties because ideas are running dry, they may direct activity into Green Hat thinking. When contingency plans are needed, they will ask for Black Hat thinking, etc.
A variant of this technique is to look at problems from the point of view of different professionals (e.g. doctors, architects, sales directors, etc.) or different customers.
This Technique is created by Edward de Bono in his book "6 Thinking Hats".
Wednesday, November 15, 2006
The 20th International Conference on Industrial, Engineering and Other Applications of Applied Intelligent Systems
Kyoto (Japan) – Kyoto University Clock Tower Hall, June 2007
Important Dates
Paper Submission: November 18, 2006 (extended)
(Abstract Submission Deadline: November 15, 2006)
Notification: February 1, 2007
Camera-ready due: February 28, 2007
Conference: June 25-28, 2007
Important Dates
Paper Submission: November 18, 2006 (extended)
(Abstract Submission Deadline: November 15, 2006)
Notification: February 1, 2007
Camera-ready due: February 28, 2007
Conference: June 25-28, 2007
Sunday, November 12, 2006
SPC
SPC is the primary and one of the best techniques for controlling and improving product or service quality methodically, which is applicable for any type of organization. It is a powerful tool of TQM that can clear the distinction between a stable process and an unstable process. It uses from Flow charts, Run charts, Pareto charts, Cause-and-effect diagrams, Frequency histograms, Scatter diagrams, Control charts, Acceptance sampling techniques and check sheets.
Process capability (CPk) is defined as the characteristics associated with the output of that process consistently conform to requirements.
Benefits
- A technique for improving quality,
- Effective in defect prevention,
- Prevents unnecessary process adjustments,
- Provides diagnostic information,
- Provides information about process capability.
Friday, November 10, 2006
JOB NEWS
Growing building products manufacturing company in Orange County, CA is currently seeking qualified candidates for the position of Process Development and Engineering Manager. This position reports to the Chief Operating Officer and will be responsible for process improvement and development at the company's current facility, support for new product development and introductions, support for facility expansion and third party manufacturer evaluations. · Design, develop, implement and maintain manufacturing processes.· Apply improvement methodologies (i.e., Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma) to products or production processes to improve product quality and/or production efficiency. · Work on cost reduction projects to reduce material/ process costs by defining and implementing new techniques and equipment/ fixtures for assembly and test. This may require designing fixtures and implementing in manufacturing facility. · Manage quality improvement process and select and manage appropriate product standards and testing procedures. Identify, develop, and implement techniques for assembly and test, including test fixtures, with Building Code Council and validating new processes, evaluate failure data from field to find root cause and implement sound engineering solutions. · Develop and ensure compliance with corporate quality system and all relevant internal procedures and policies.· Responsible for training techs and assemblers and supporting transfer of product into manufacturing facilities. · Provide continuous engineering support on assigned products to maintain and improve margin, performance and quality. · Work to deliver acceptable documentation on product (including but not limited to: Assembly and test fixtures, Test methods, Drawings and Specs) in a timely manner. · Provide process and project support for new business initiatives.· Assist with specification and evaluation of third party manufacturing facilities.REQUIREMENTS The essential requirements for this position are a BS or MS degree in Engineering and at least five years work experience in related field. Familiarity with the ISO 9001 and other relevant standards. Training in Lean Manufacturing and/or Six Sigma methodologies. The desirable requirements for this position are experience in composite molding and concrete products manufacturing. Excellent communication skills, and problem solving skills. Ability to plan and schedule multiple projects and tasks. Fluent in Spanish a plus. Need to be able to make rapid and sound decisions. Good knowledge of MS Office Suite and MS Project. Be able to work with people at all levels of organization. UPDATE: Does not want from the following industries:
1. Medical devises
2. Automotive
3. Aerospace
Client is looking for someone from "dirty" manufacturing.
1. CNC - computer numerical control
2. Plastic Injection
3. Molding or Die Casts
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
